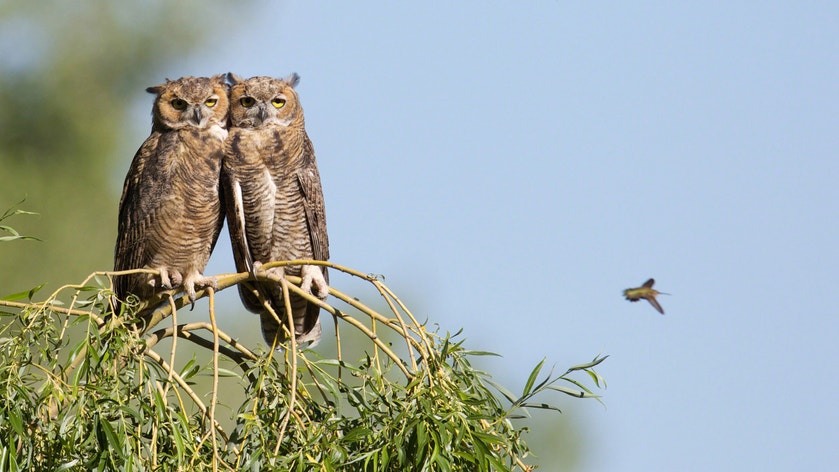
Great Horned Owl
At a Glance
Found almost throughout North America and much of South America is this big owl. Aggressive and powerful in its hunting (sometimes known by nicknames such as 'tiger owl'), it takes prey as varied as rabbits, hawks, snakes, and even skunks, and will even attack porcupines, often with fatal results for both prey and predator. Great Horned Owls begin nesting very early in the north, and their deep hoots may be heard rolling across the forest on mid-winter nights.
All bird guide text and rangemaps adapted from Lives of North American Birds by Kenn Kaufman© 1996, used by permission of Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Category
Owls
IUCN Status
Least Concern
Habitat
Coasts and Shorelines, Desert and Arid Habitats, Fields, Meadows, and Grasslands, Forests and Woodlands, Freshwater Wetlands, High Mountains, Shrublands, Savannas, and Thickets, Tundra and Boreal Habitats, Urban and Suburban Habitats
Region
Alaska and The North, California, Eastern Canada, Florida, Great Lakes, Mid Atlantic, New England, Northwest, Plains, Rocky Mountains, Southeast, Southwest, Texas, Western Canada
Population
5.700.000
Range & Identification
Migration & Range Maps
No regular migration, but individuals may wander long distances in fall and winter, some of them moving southward.
Description
25" (64 cm). W. 4' 7 (1.4 m). Large size, conspicuous "ear" tufts, white throat, horizontal bars on belly. Compare to smaller Long-eared Owl. Downy young (like those of other owls) are whitish at first.
Size
About the size of a Mallard or Herring Gull, About the size of a Heron
Color
Brown, Gray, Red, Yellow
Tail Shape
Rounded, Short, Square-tipped
Songs and Calls
Series of low, sonorous, far-carrying hoots, hoo, hoo-hoo, hoo, hoo, with second and third notes shorter than the others.
Habitat
Forests, woodlots, streamsides, open country. Found in practically all habitats in North America, from swamps to deserts to northern coniferous forest near treeline. In breeding season avoids tundra and unbroken grassland, since it requires some trees or heavy brush for cover.
Sign up for Audubon's newsletter to learn more about birds like the Great Horned Owl
Behavior
Eggs
2-3, sometimes 1-5, rarely 6. Dull whitish. Incubation mostly by female, 28-35 days.
Young
Both parents take part in providing food for young owls. Young may leave nest and climb on nearby branches at 5 weeks, can fly at about 9-10 weeks; tended and fed by parents for up to several months.
Feeding Behavior
Hunts mostly at night, sometimes at dusk. Watches from high perch, then swoops down to capture prey in its talons. Has extremely good hearing and good vision in low light conditions. In north in winter, may store uneaten prey, coming back later to thaw out frozen carcass by "incubating" it.
Diet
Varied, mostly mammals and birds. Mammals make up majority of diet in most regions. Takes many rats, mice, and rabbits, also ground squirrels, opossums, skunks, many others. Eats some birds (especially in north), up to size of geese, ducks, hawks, and smaller owls. Also eats snakes, lizards, frogs, insects, scorpions, rarely fish.
Nesting
May begin nesting very early in north (late winter), possibly so that young will have time to learn hunting skills before next winter begins. In courtship, male performs display flight, also feeds female. Nest: Typically uses old nest of other large bird, such as hawk, eagle, crow, heron, usually 20-60' above ground; also may nest on cliff ledge, in cave, in broken-off tree stump, sometimes on ground. Adds little or no nest material, aside from feathers at times.
Conservation
Conservation Status
Widespread and common, numbers apparently holding up well in most areas.
Climate Threats Facing the Great Horned Owl
Choose a temperature scenario below to see which threats will affect this species as warming increases. The same climate change-driven threats that put birds at risk will affect other wildlife and people, too.