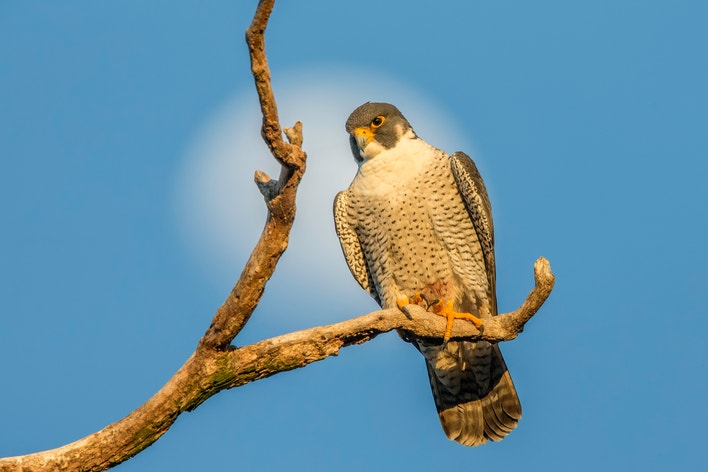
Peregrine Falcon
At a Glance
One of the world's fastest birds; in power-diving from great heights to strike prey, the Peregrine may possibly reach 200 miles per hour. Regarded by falconers and biologists alike as one of the noblest and most spectacular of all birds of prey. Although it is found on six continents, the Peregrine is uncommon in most areas; it was seriously endangered in the mid-20th century because of the effects of DDT and other persistent pesticides.
All bird guide text and rangemaps adapted from Lives of North American Birds by Kenn Kaufman© 1996, used by permission of Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Category
Falcons, Hawk-like Birds
IUCN Status
Least Concern
Habitat
Arroyos and Canyons, Coasts and Shorelines, Fields, Meadows, and Grasslands, Freshwater Wetlands, Lakes, Ponds, and Rivers, Saltwater Wetlands, Tundra and Boreal Habitats, Urban and Suburban Habitats
Region
Alaska and The North, California, Eastern Canada, Florida, Great Lakes, Mid Atlantic, New England, Northwest, Plains, Rocky Mountains, Southeast, Southwest, Texas, Western Canada
Behavior
Direct Flight, Flap/Glide, Soaring
Population
340.000
Range & Identification
Migration & Range Maps
Permanent resident on northwest coast and in some temperate regions; northern breeders are long-distance migrants, many going to South America. Migrants often travel along coastlines and regularly occur well out at sea.
Description
15-21" (38-53 cm). W. 3' 4 (1 m). Large and powerful, with typical pointed-winged falcon silhouette. Flies with strong shallow wingbeats; when diving on prey, may reach speeds of well over 100 mph. Usually looks quite dark (although Arctic birds are paler), with dark hooded effect. Adults blue-gray above, narrowly barred below; juveniles browner, streaked below.
Size
About the size of a Crow, About the size of a Mallard or Herring Gull
Color
Black, Brown, Gray, White, Yellow
Wing Shape
Long, Pointed, Swept, Tapered
Tail Shape
Long, Rounded, Square-tipped
Songs and Calls
Rasping kack-kack-kack-kack, usually heard at nest; otherwise generally silent.
Call Pattern
Flat, Simple
Call Type
Scream
Habitat
Open country, cliffs (mountains to coast); sometimes cities. Over its wide range, found in wide variety of open habitats, from tundra to desert mountains. Often near water, especially along coast, and migrants may fly far out to sea. Limited by availability of nest sites and prey; thus, it often moves into cities, nesting on building ledges and feeding on pigeons.
Sign up for Audubon's newsletter to learn more about birds like the Peregrine Falcon
Behavior
Eggs
3-4, sometimes 2-5, rarely 6. Whitish to pale reddish-brown, heavily marked with warm brown. Incubation is mostly by female, 32-35 days. Male brings food for female during incubation.
Young
Female stays with young at first, while male brings food for her and for young; later, female hunts also. Age of young at first flight 39-49 days.
Feeding Behavior
Often hunts by flying very high, then stooping in spectacular dive to strike prey out of the air. Large prey may be knocked out of the air, fed upon on the ground where it falls. Also pursues prey in level flight, after having spotted it from a perch or while flying. May fly very low over ground or sea, taking prey by surprise.
Diet
Mostly birds. Feeds on a wide variety of birds. Pigeons are often favored prey around cities, and ducks and shorebirds often taken along coast; known to take prey as large as loons, geese, large gulls, and as small as songbirds. Also eats a few small mammals, seldom insects, rarely carrion.
Nesting
May mate for life. Territorial and courtship displays include high circling flight by male, spectacular dives and chases by both sexes. Male feeds female. Breeding Peregrines defend the immediate area of the nest from intruders, but hunt over a much larger area. Nest site is usually on cliff ledge, sometimes in hollow of broken-off tree snag or in old stick nest of other large bird in tree. In some areas, may nest on ground on hilltop. Also uses ledges of buildings, bridges, other structures. Some sites may be used for many years. No nest built, eggs laid in simple scrape.
Conservation
Conservation Status
Concentrations of pesticides from its prey caused widespread failure to reproduce during 1940s-1970s, and species disappeared from much of former breeding range. Has been reintroduced in many temperate areas in North America, and Arctic nesting populations have recovered somewhat also. Current populations appear to be stable or increasing.
Climate Threats Facing the Peregrine Falcon
Choose a temperature scenario below to see which threats will affect this species as warming increases. The same climate change-driven threats that put birds at risk will affect other wildlife and people, too.